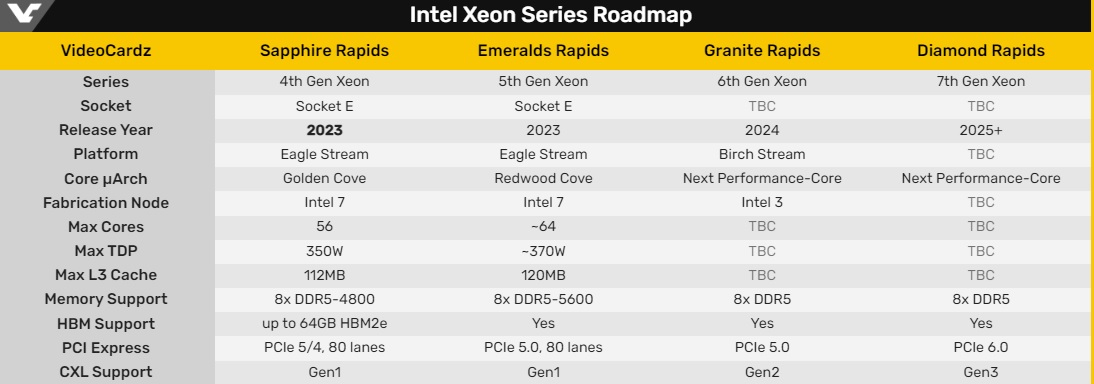
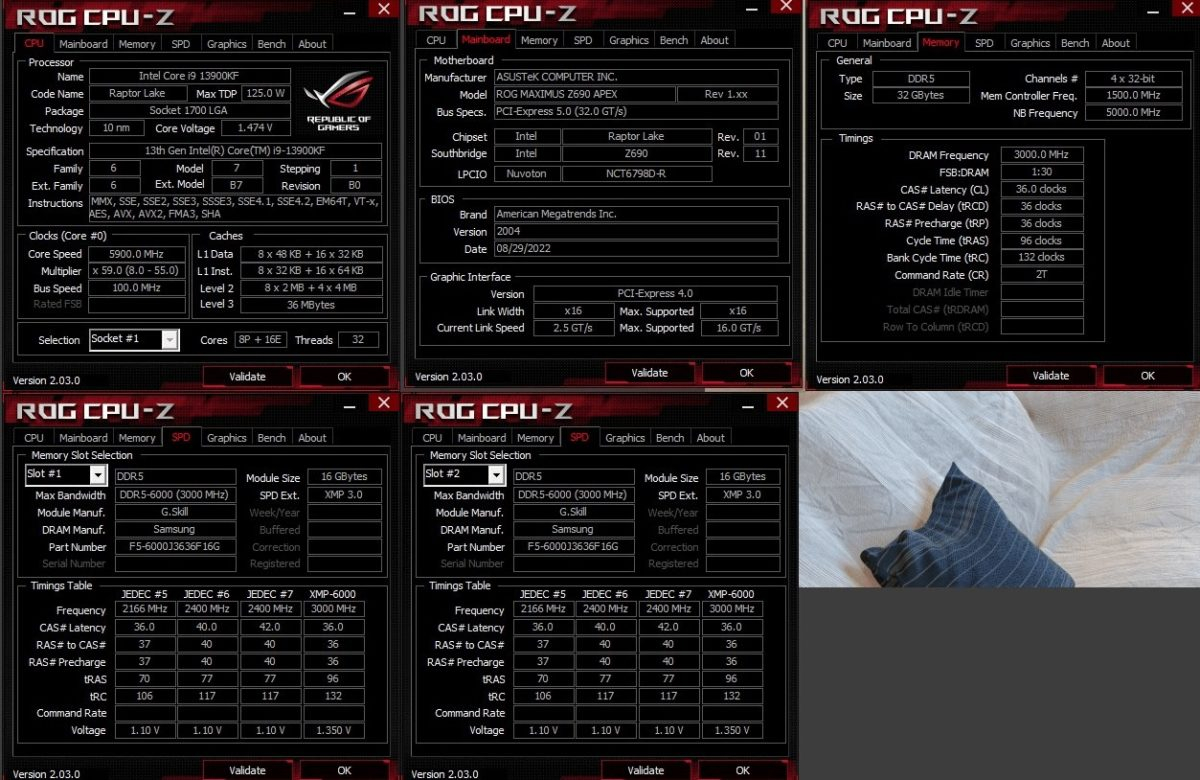
Chinese processor developers are making serious bets on Arm and RISC architectures, since access to them has so far not been restricted by political opponents.But now Arm has refused to export Neoverse V architecture licenses to China and this could become a nasty precedent, limiting the pace of development of China's national semiconductor industry.Image source: AlibabaBritish Arm holding, as the Financial Times reports, has determined that Chinese customers cannot buy licenses to use Neoverse V processor architectures because they allow processors to be built at performance levels that exceed the values allowed by US export rules.The Neoverse V architecture includes elements developed in the United States, so British Arm has to negotiate the nuances of exporting the relevant technology with overseas officials.As expected, the Chinese giant Alibaba as a result of such restrictions may face the inability to use the Neoverse V1 or V2 architecture in its processors.In this case, the Chinese partners of Arm will be available architecture series Neoverse N2, which has a lower speed.This situation resonates with the restrictions, which have already faced NVIDIA, which lost the right to supply after the fall of next year, gas pedals generation calculations Ampere and Hopper with a certain level of performance.The supplier was quick to react and started offering Chinese customers special A800 gas pedals, whose performance avoided the sanctions restrictions by a margin.Arm's Chinese customers found themselves in a similar situation.The same company, Alibaba, expected to buy a license from Arm to use the Neoverse V1 architecture to develop processors used in cloud systems.Competitor Amazon Web Services in the U.S.already uses the architecture of this series to create specialized processors used in its own infrastructure.Alibaba representatives, on condition of anonymity, expressed dissatisfaction with Arm's behavior, stating its reluctance to sell technology to China even if such deals are adequately funded.