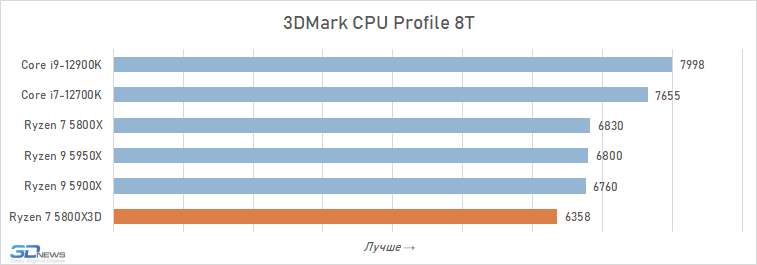
Ryzen processors with 3D V-Cache technology, which expands cache memory with additional SRAM semiconductor crystal, were first mentioned by AMD exactly one year ago - at Computex 2021.And at that time, this announcement has created a real furore.On the one hand, through it AMD has confirmed its technological potential, as it showed its readiness to introduce an advanced technology of 3D-mounting of semiconductor chips and expand the chip design of its processors in the vertical direction.On the other hand, it has promised to significantly strengthen the Ryzen 5000 series by the end of 2021, adding a flagship 12-core processor with a giant cache and significantly increased performance in gaming applications.However, these Napoleonic plans - at least in their original form - were not fated to materialize.Promised Ryzen 9 5900X with 3D V-Cache technology never came out, and instead of it AMD released another consumer CPU with increased cache according to this technology - Ryzen 7 5800X3D.And it frankly looks a lot less spectacular. Firstly, Ryzen 7 5800X3D is just an octa-core CPU, which obviously cannot be a universal flagship solution, because 12- and 16-core solutions have been widely available in the desktop segment for a long time.Secondly, by the end of this year there will be more progressive processors based on Zen 4 microarchitecture in AMD's arsenal, which will almost certainly eclipse the Ryzen 7 5800X3D due to the IPC index growth and DDR5 SDRAM support.And third, with the introduction of the Alder Lake family late last year, the leadership in desktop processor performance has gone to Intel.Because Alder Lake offers higher specific performance than Zen 3, Ryzen 7 5800X3D now has to solve a completely different problem: it does not set new performance records in games, but only tries to catch up with competitor processors in an extensive way - by multiplying the amount of cache memory.In other words, the Ryzen 7 5800X3D output ended up being quite stripped out, and it seems that AMD lost a lot from the fact that it missed the deadline and made the model not at all what it promised.Nevertheless, that doesn't stop it from touting the Ryzen 7 5800X3D as \"the world's fastest gaming processor.\" However, there is a feeling that AMD overestimates the capabilities of its product: at least, many independent reviews could not confirm AMD's rightness in performance evaluations of the novelty.And for this reason we decided to test Ryzen 7 5800X3D with our own hands.Moreover it is not only unique by its design AMD processor, but also a kind of a final line in the history of Socket AM4 ecosystem: its development on Ryzen 7 5800X3D stops completely and no other CPU models will be available for this socket anymore.⇡# 3D V-Cache in detailsThe idea to expand cache capacity for better performance obviously did not come from AMD out of nowhere.Moving large amounts of data closer to the processor cores, which dramatically increases the speed of access to them - a fairly simple trick, which AMD liked before.AMD processors have long been distinguished by the amount of cache memory, and the company's marketing department uses the name Game Cache for it, explicitly stating that a capacious L3 cache is extremely useful for games.The opposite is also true: Ryzen processors with reduced cache, such as Ryzen 5 5500, have rather modest gaming performance.Ryzen 7 5800X3D is a processor where the idea of increasing cache capacity in the name of maximum FPS is taken to the absolute limit: it has 96 MB of L3 per eight cores (12 MB per core).But its main peculiarity is not even the impressive size of the cache, but the design, which is figuratively described in the model number of the processor with the ending \"3D\".It means that in the Ryzen 7 5800X3D cache is expanded with an additional 3D V-Cache crystal, which is physically superimposed on the original processor chip on top - in the third dimension.In words it sounds quite simple: an additional 64 MB SRAM chip is mounted on top of the 32 MB L3 cache present in the CPU chip and connected to it through connections.But in reality it is much more complicated. To place the superstructure in the form of a 3D-cache crystal on the processor chip, AMD had to work with TSMC on a special production technology, which would reduce the thickness of the combined from two parts - CCD (Core Complex Die) and 3D-cache - integrated device.As a result, it is reduced to the height of a single chip of conventional processors, so Ryzen 7 5800X3D fits into exactly the same package as other Ryzen family processors and does not require any special cooling systems or their mounts.This is achieved by two techniques.First


0 Comments