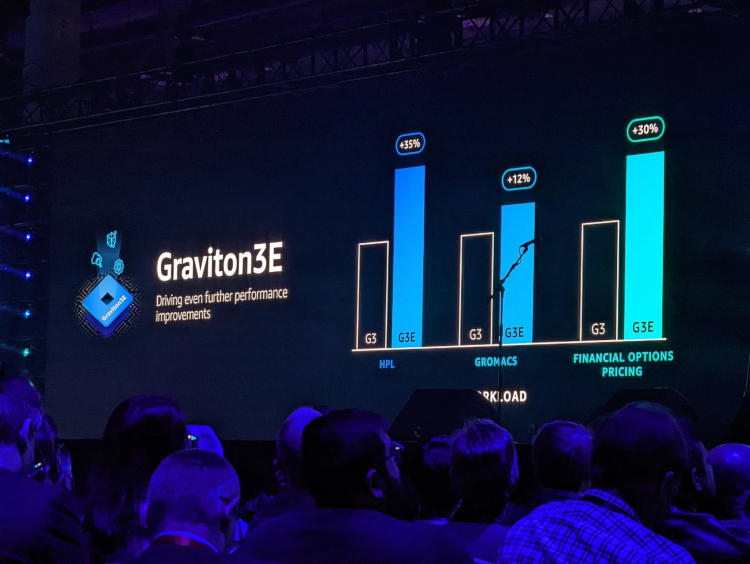
Amazon Web Services (AWS) announced a number of new products: an optimized high performance computing (HPC) Arm processor Graviton3E, an updated hypervisor Nitro capable of handling more traffic, and a network protocol designed for its operation.Image source: techcrunch.comThe new processor is named Graviton3E - it is optimized for floating point and vector calculations, that is, the most demanded operations in the world of high-performance computing.The company did not yet specify the chip's specifications, but said that in tests reflecting work for life science and financial disciplines, it performs better than the base Graviton3.HPC workloads are traditionally associated with transferring large amounts of data, and to optimize this process the company announced a network interface EFA (Elastic Fabric Adapter).It was complemented by the SRD (Scalable Reliable Datagram) networking protocol, which is an alternative to TCP.The AWS back-end infrastructure uses multipath routing, which is not supported by TCP in a basic implementation, and this affects performance.SRD solves the problem by allowing packets to be transmitted out of order and ordered by acceptance - with lost packets transmitted in \"micro-not milliseconds,\" the company specified, and it speeds up networks in the AWS cloud infrastructure.The company also announced an updated version of its Nitro hypervisor (fifth generation) with SRD support, offering nearly double the processing power: DRAM throughput increased by 50%, PCIe throughput doubled, the number of packets transferred per second increased by 60%, and latency reduced by 30%.AWS announced instances like C7GN with Graviton3 and Nitro v5, and HPC7G with Graviton3E and Nitro v5.Finally, the company talked about improvements to its serverless AWS Lambda environment - it is built on small virtual machines occupying \"slots\" on the host.The provider always tries to keep these machines running as long as possible, because their \"cold start\" takes quite a long time, and this can discourage users.To achieve a balance, AWS has developed SnapStart technology that takes a snapshot of the Lambda function and caches it.When the Lambda function is called later, SnapStart resumes the execution environment immediately from the cached snapshot, rather than initializing it from scratch, thus reducing startup latency.


0 Comments