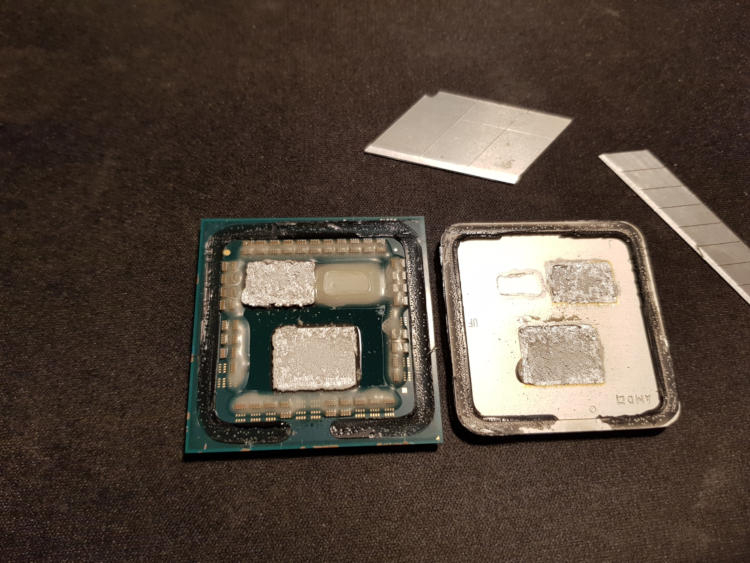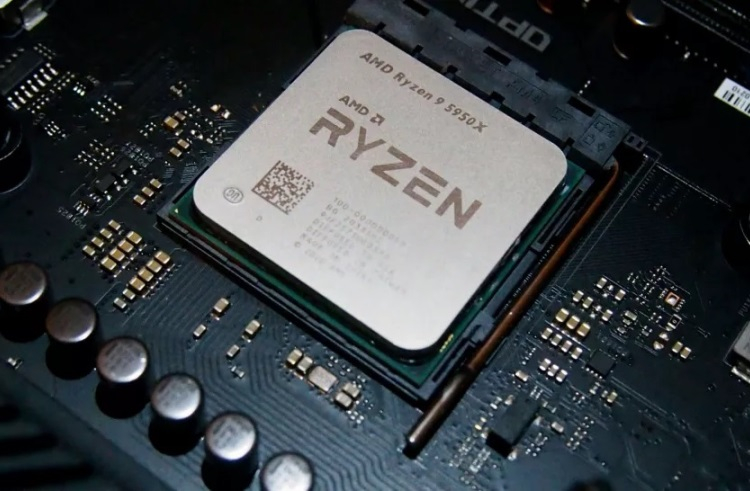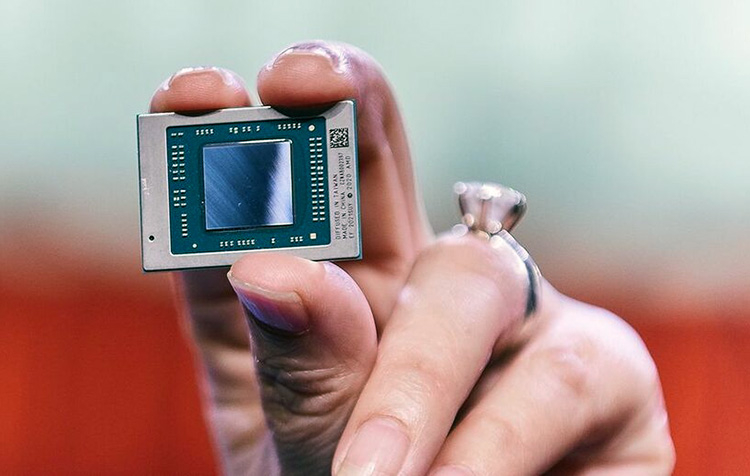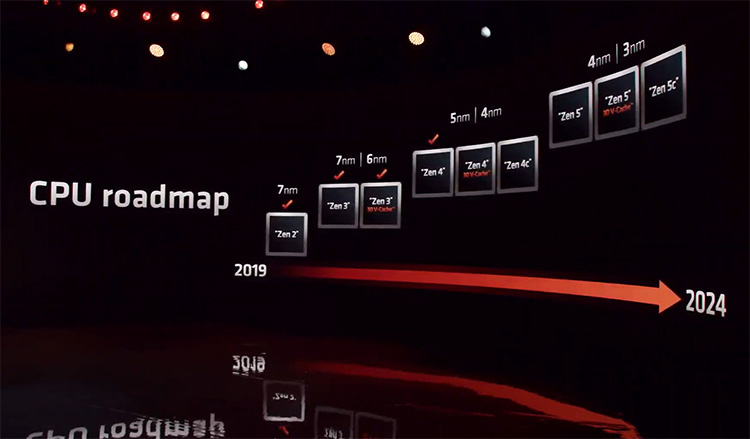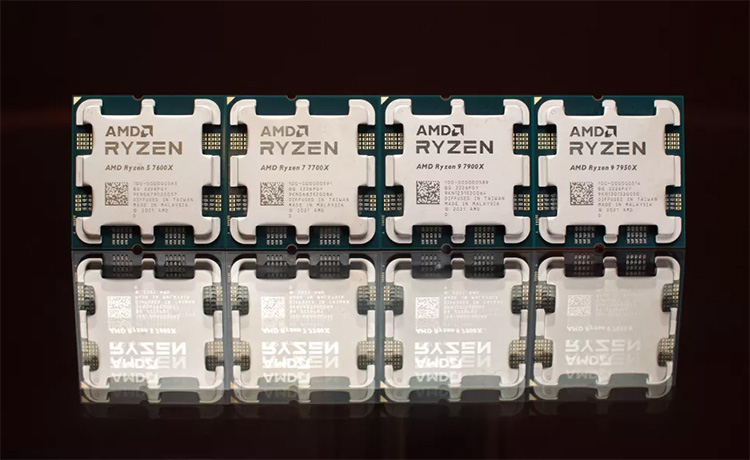
Announcing the Ryzen 7000 family of desktop processors, AMD CEO Lisa Su assured that no shortage is expected at the start of sales.In her opinion, everyone will be able to buy the new products after September 27.Commenting on the availability of Ryzen 7000 on sale, Lisa Su said: \"If you look at the situation over the past 18 months, you can see a lot of problems, whether it's a lack of production capacity or logistical disruptions.Right now, on AMD's part, we've had a serious increase in production volumes in terms of both semiconductor wafers and wafers.So in the case of the Zen 4 launch we do not expect any supply constraints\".The Ryzen 7000 processors are scheduled for September 27, and AMD has a month to fill up supply channels.That's time AMD will spend, Lisa Su said, to get the new products to store shelves around the world and just in time. It is worth recalling that AMD has suspended the supply and official sales of its processors in Russia since the beginning of March.Therefore, new AMD processors may appear in local stores only through parallel import with some delay.Ryzen 7000 processors for desktops are based on Zen 4 architecture and due to IPC and clock speeds growth offer 29 % performance increase comparing to their predecessors.They support PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 memory.The lineup includes four models with the number of cores from 6 to 16 and price from $300 to $700.